decentralized finance (dE-fi)

<> DeFi stands for “decentralized finance,” though it’s also known as “open finance.”
It’s a financial system in which middlemen are removed and, like most things associated with Web3, is a utopian vision of a financial system that operates without a central authority.
<> Decentralized finance (DeFi) is an emerging financial technology based on secure distributed ledgers similar to those used by cryptocurrencies.
<> The system removes the control banks and institutions have on money, financial products, and financial services.

Some of the key attractions of DeFi for many consumers are:
- It eliminates the fees that banks and other financial companies charge for using their services.
- You hold your money in a secure digital wallet instead of keeping it in a bank.
- Anyone with an internet connection can use it without needing approval.
- You can transfer funds in seconds and minutes anonymously.
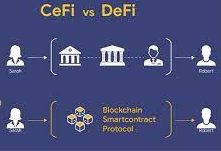
Centralized Finance vs. Decentralized Finance?
Definition: short for decentralized finance, DeFi is an umbrella term for peer-to-peer financial services on public blockchains.
<> As the name suggests, decentralized finance is the opposite of centralized finance, which is the system we now operate under—at least most people do, most of the time.
<> For example, if you buy something from an online store and pay with your credit card, the credit card company and your bank act as middlemen before the money ends up in the coffers of the shop you’re in.
<> In the scenario proposed by most proponents of DeFi, instead of using your card, you would use some form of cryptocurrency and circumvent the fees demanded by the credit card company and the bank.
<> DeFi applications would instead rely on so-called stablecoins like Dai or Tether. These currencies are usually pegged to an existing real-world fiat currency, often the U.S dollar, and generally don’t show the crazy spikes upward and downward of Bitcoin.
<> Smart contracts are also an interesting new development. They’re decentralized apps, or dApps, existing on a blockchain (usually the Ethereum blockchain), self-contained little programs that fire when agreed-upon conditions are met—that’s the “smart” bit. However once the deal is made, it can’t be altered.

What are some benefits of DEFI?
DeFi would extend much more than just paying for online goods and services; it aims to take banks out of the equation entirely.
-
Open: You don’t need to apply for anything or “open” an account. You just get access by creating a wallet.
-
Pseudonymous: You don’t need to provide your name, email address, or any personal information.
-
Flexible: You can move your assets anywhere at any time, without asking for permission, waiting for long transfers to finish, and paying expensive fees.
- Transparent: Everyone involved can see the full set of transactions (private corporations rarely grant that kind of transparency)
Under DeFi, you could make a deal with somebody online, set down the terms and conditions in a smart contract and then go from there. Instead of dealing with a bank or some other kind of loan company, you’d just deal with another individual.
Source: Youtube.com
Common problems with De-Fi
One big issue is the reliance on cryptocurrency. These currencies are inherently unstable, even stablecoins: most stablecoins see some fluctuation over time, just not as dramatic as Bitcoin’s shifts.
- Paying a loan off in gets to be worth more, this would make your loan more expensive, a scary thought.
-
Fluctuating transaction rates on the Ethereum blockchain mean that active trading can get expensive.
-
Depending on which dapps you use and how you use them, your investment could experience high volatility – this is, after all, new tech.
-
You have to maintain your own records for tax purposes. Regulations can vary from region to region.
- Scams are common, and it’s far too easy to get away with not paying people or otherwise shirking payments and the like.
DeFi is still very much a playground for people that like risk. If that’s not you, you may want to stay away from it for now, and crypto and NFTs in general. That said, if you like the cutting edge, then DeFi might be the place for you.

Ways people are engaging with DeFi today
Users typically engage with DeFi via software called dapps (“decentralized apps”), most of which currently run on the Ethereum blockchain.
Unlike a conventional bank, there is no application to fill out or account to open.
Ethereum allows complete financial freedom – most products will never take custody of your funds, leaving you in control.
You can think of DeFi in layers:
- ) The blockchain – Ethereum contains the transaction history and state of accounts.
- ) The assets – ETH and the other tokens (currencies).
- ) The protocols – smart contracts that provide the functionality, for example a service that allows for decentralized lending of assets.
- ) The applications – the products we use to manage and access the protocols.
Ethereum is the perfect foundation for DeFi for a number of reasons:
Lending: Lend out your crypto and earn interest and rewards every minute – not once per month.
Getting a loan: Obtain a loan instantly without filling in paperwork, including extremely short-term “flash loans” that traditional financial institutions don’t offer.
Trading: Make peer-to-peer trades of certain crypto assets — as if you could buy and sell stocks without any kind of brokerage.
Buying derivatives: Make long or short bets on certain assets. Think of these as the crypto version of stock options or futures contracts.
- Tokens and cryptocurrency are built into Ethereum, a shared ledger – keeping track of transactions and ownership is kinda Ethereum’s thing.