what is a blockchain ?
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are powered by a technology called the blockchain.
At its most basic, a blockchain is a list of transactions that anyone can view and verify. The Bitcoin blockchain, for example, contains a record of every time someone sent or received bitcoin.
Cryptocurrencies and the blockchain technology that powers them make it possible to transfer value online without the need for a middleman like a bank or credit card company.
-
Almost all cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, Bitcoin Cash, and Litecoin, are secured via blockchain networks. Which means their accuracy is constantly being verified by a huge amount of computing power.
-
The list of transactions contained in the blockchain is fundamental for most cryptocurrencies because it enables secure payments to be made between people who don’t know each other without having to go through a third-party verifier like a bank.
-
Due to the cryptographic nature of these networks, payments via blockchain can be more secure than standard debit/credit card transactions. When making a Bitcoin payment, for instance, you don’t need to provide any sensitive information. That means there is almost zero risk of your financial information being compromised, or your identity being stolen.




How does a blockchain work ?
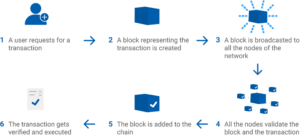
As the name suggests, Blockchains are formed from a chain of blocks, each of which store information. The exact information they store differs between blockchains. Bitcoin, as an example, contains information about the total BTC being transferred as well as the sender and receiver.
The core elements on which blockchain technology operates are its distributed ledger technology, immutable records and smart contracts.
Immutable records
Immutable records, mean that the information on a blockchain network can’t be changed without re-writing all of the following blocks.
Every single transaction that occurs through smart contracts and payments are scrutinized by other nodes within that network to ensure their authenticity and validity.
Smart Contracts
The interconnected nature of the blockchain allows for smart contract agreements that are automatically executed once their requirements are met, such as receiving payment or certifying a certain data point has been collected.
It’s an agreement set out in coded language through which two parties agree to perform or not perform some action. If the transaction takes place between known entities, smart contracts make it easier to verify the rules are upheld.
Smart contracts can be created for anything from property sales to car rentals, smart energy grids and even employee contracts.
Types of Distributed Ledger Technologies
There are two distinct types of distributed ledgers and blockchains: permissioned (private) and permissionless (public).
In essence, this determines who can participate in validating transactions on the network.
In a permissionless distributed ledger, anyone can join the network without needing to be approved by anyone, like in the case of Bitcoin or Litecoin.
A permissioned ledger requires participants to be approved before they can be part of the network, for example Facebooks’ Diem stablecoin project (formerly known as Libra).
Blockchain vs Distributed Ledger Technology
There are numerous blockchain networks and platforms out there, but we’ll look at two of the most well-known. Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) are two of the most popular consensus mechanisms used on blockchains.
What is Bitcoin Blockchain?
The Bitcoin blockchain uses a Proof-of-Work consensus algorithm. With Bitcoin’s blockchain network, every time someone sends BTC from one account to another the transaction is encoded into a block containing all of the information about the transaction, including the time and date of transfer.
What is Ethereum Blockchain?
Ethereum is looking to move to a Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm. Ethereum is an open-source blockchain, that features its own cryptocurrency, ETH. It works in a similar way to Bitcoin and other blockchains, but it is versatile and has many more applications; it allows developers to write smart contracts that operate on the blockchain. This means transactions can be encoded into blocks and stored permanently, without risk of being deleted or tampered with by unauthorised parties.
What Is Mining?
A process where blocks are added to a blockchain, verifying transactions. It is also the process through which new bitcoin or some altcoins are created.
What are the Blockchain advantages?
Blockchain provides many advantages over conventional methods of transactions and record-keeping, including:
Security
A major benefit of blockchain technology is its security. Because there is no central location for the blockchain network, if a hacker wanted to break into a smart contract or smart property, they would have to gain access to every computer in the chain at the same time. This makes it extremely unlikely that any cybercriminal will ever penetrate your smart contract or smart property.
Speed
The blockchain network is able to process transactions in real-time, which is why many believe it will become an integral part of the future financial system.
Cost-effective
Blockchain could potentially eliminate the need for banks and other third parties that often add significant costs to the consumer. The blockchain model is designed in a way that reduces or eliminates the need for intermediaries, which not only saves time and money but also prevents delays in processes.

“serious copywriting chops and a fabulous sense of humor”


- Security and transparency
- No intermediaries needed
- Permissionless system state
- Data integrity & reliability
Use of Distributed Ledgers
Distributed ledgers have shown that they have what it takes to be used by private corporations, governments and institutions.
Governments can utilize decentralized ledgers to minimize fraud, data security and streamline processes.
The technology can be used in several industries such as:
- Finance (Capital Markets)
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P)
- Secure sharing of medical data.
- NFT marketplaces.
- Music royalties tracking.
- Cross-border payments.
- Real-time IoT operating systems.
- Personal identity security.
- Anti-money laundering tracking system.
- Manufacturing, Supply chain and logistics monitoring.
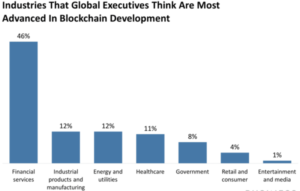
To understand what blockchain is, one needs to imagine a virtual ledger capable of registering and verifying a huge number of electronic transactions quickly and safely. Today, this shared ledger technology has greatly expanded the area of application.